DSCOVR Satellite – Our gatekeeper in the sky
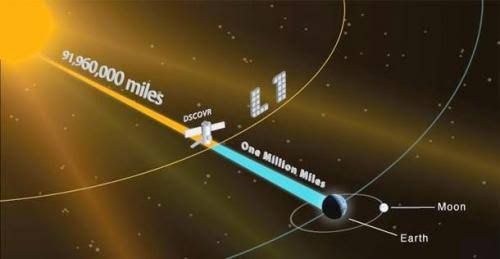
DSCOVR (short for Deep Space Climate Observatory) is a special satellite that watches the Sun and helps us prepare for space weather. It was launched in 2015 and sits in space at a spot called Lagrange Point 1, or L1 — that’s about 1.5 million kilometres (or about a million miles) away from Earth, between us and the Sun.
This spot is special because gravity from the Earth and the Sun balance out, so the satellite can “hover” there without falling toward either one.
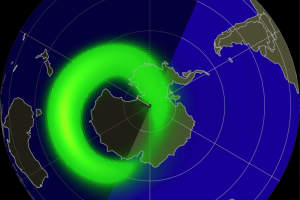
DSCOVR’s main job is to watch the solar wind — streams of particles from the Sun — and give us early warnings when big solar storms (CMEs) are coming our way. These storms can mess with satellites, power lines, internet, and radio signals here on Earth.
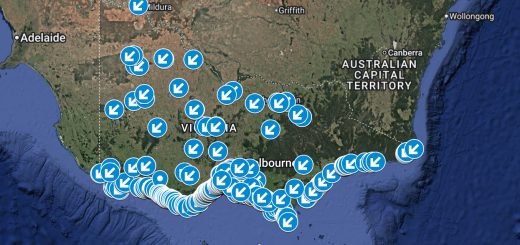
Most Aurora apps use live data from DSCOVR to help forecast when and where we might see the Northern or Southern Lights.
DSCOVR sends this info to NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center, which uses it to send out alerts to protect our technology from space weather.